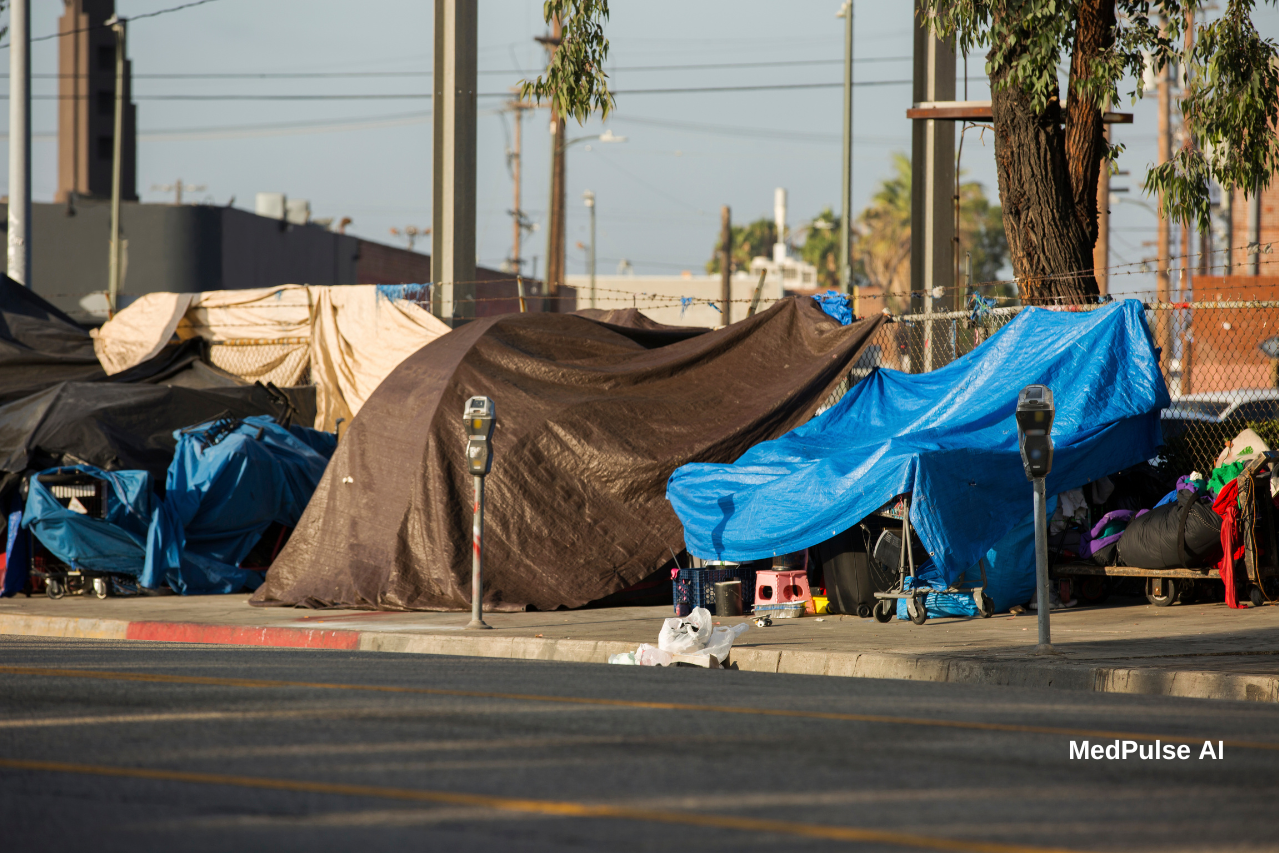
In Los Angeles, a city with one of the largest unhoused populations in the United States, accessing quality healthcare is a significant challenge. For those facing housing insecurity, barriers such as lack of documentation, mistrust of the medical system, and constant mobility often result in gaps in treatment. These challenges frequently lead to deteriorating health and prevent access to consistent care.
Dr. Steven Hochman, a dedicated street medicine physician, is tackling these challenges head-on by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into his practice. By combining cutting-edge technology with compassionate care, Dr. Hochman is redefining healthcare delivery for unhoused and resource-poor individuals, setting a precedent for how technology can bridge healthcare inequities.
The State of Healthcare for the Unhoused
The number of displaced individuals in Los Angeles exceeds 40,000, many of whom suffer from chronic illnesses, mental health conditions, and substance use disorders. For these individuals, accessing healthcare often feels like navigating an insurmountable maze. Common obstacles include:
- Lack of Identification: Without proper documentation, many unhoused individuals cannot access traditional healthcare services.
- Mobility Challenges: Frequent relocations make it difficult to maintain continuity of care.
- Limited Trust: Stigmatization and discrimination have contributed to a widespread mistrust of healthcare providers among individuals facing housing insecurity.
- Logistical Barriers: Issues such as lack of transportation and inflexible clinic hours further limit access.
These systemic issues not only perpetuate health disparities but also strain public healthcare resources, as many individuals rely on emergency rooms for treatable or preventable conditions. This is where innovative solutions like AI-powered street medicine come into play.
Collaborating with Akido Labs, a tech-focused healthcare organization, Dr. Hochman conducts weekly visits to encampments, utilizing AI tools to streamline patient care. Akido Labs has developed a proprietary AI system that transcribes patient interactions and generates detailed reports. This technology enables Dr. Hochman to efficiently document medical histories and coordinate care, allowing him to focus more on patient engagement. The AI system also assists in managing patient records, scheduling medication deliveries, and summarizing clinical conversations, thereby improving the overall efficiency of street medicine practices.
Here are the key ways AI is making a difference:
- Efficient Documentation:
- Using natural language processing (NLP) algorithms, the AI transcribes patient interactions into detailed medical records.
- This eliminates the need for manual note-taking, enabling Dr. Hochman to focus on building trust and understanding patients’ immediate health needs.
- Seamless Coordination:
- The AI system centralizes patient information, helping manage medical histories and track ongoing treatments even when patients are constantly on the move.
- This ensures continuity of care, a crucial aspect for homeless individuals who often face disruptions in accessing healthcare.
- Medication Management:
- AI tools schedule medication deliveries and send reminders for refills, helping patients adhere to treatment plans.
- This is vital for managing chronic illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension, and mental health conditions prevalent in homeless populations.
- Data Analysis for Improved Outcomes:
- The AI analyzes aggregated patient data to identify trends, predict health risks, and prioritize care interventions.
- By highlighting patterns such as recurring infections or mental health crises, the system empowers providers to take proactive steps.
The Human Side of AI-Driven Street Medicine
While AI plays a vital role in improving operational efficiency, it is Dr. Hochman’s human-centered approach that truly makes the difference. By spending more time building relationships with his patients and addressing their unique needs, he fosters trust and cooperation. This balance between technology and empathy is key to breaking down the stigma and mistrust that many homeless individuals feel toward the healthcare system.
Dr. Hochman’s weekly visits to encampments are a testament to this commitment. Equipped with AI tools, he can focus on listening to patients, diagnosing conditions, and providing immediate care. The AI system acts as a silent partner, handling administrative tasks and offering decision support, enabling him to focus solely on his patients.
Expanding the Vision: AI in Community Healthcare
The success of Dr. Hochman’s work raises the question: Can this model be scaled to other cities or healthcare contexts? The answer lies in collaboration among stakeholders. Here’s what the future might look like:
- Mobile Health Units with AI Capabilities
- Mobile clinics equipped with AI tools could provide diagnostics, telemedicine consultations, and even minor procedures in underserved areas.
- Predictive Analytics for Resource Allocation
- AI can help city planners and public health officials predict where healthcare resources, such as vaccination drives or mental health services, are needed most.
- Telehealth for the Unhoused
- With access to smartphones increasing even among homeless populations, AI-powered telehealth platforms could connect patients to remote providers.
- Community Engagement
- Partnering with local organizations to educate communities about the benefits of AI in healthcare can further reduce stigma and promote trust.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, the integration of AI into street medicine comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensuring the success and sustainability of such initiatives:
1. Data Privacy
- Handling sensitive patient information requires robust security measures. Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA is critical, especially when dealing with vulnerable populations who may already distrust institutions.
2. Algorithmic Bias
- AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the data contains biases, it could perpetuate inequities in care delivery. Regular audits and updates to the algorithms are necessary to maintain fairness.
3. Sustainability
- AI tools require significant financial and technical resources. Ensuring the long-term availability of these tools for underserved populations depends on securing consistent funding and support from both public and private sectors.
4. Technology Literacy
- Providers must be trained to use AI tools effectively, and patients need reassurance about how their data is being used. Transparent communication is key to building trust.
The collaboration between Dr. Hochman and Akido Labs exemplifies how AI can be harnessed to improve healthcare access for underserved communities, highlighting the potential of technology to bridge gaps in medical care for individuals facing housing insecurity.