Cervical cancer remains a significant global health issue, ranking as the fourth most common cancer among women worldwide. In 2022 alone, approximately 660,000 new cases were reported, leading to about 350,000 deaths . The good news is that cervical cancer is one of the most treatable forms of cancer if detected early and managed effectively. However, various challenges in screening and treatment processes can hinder timely diagnosis and intervention. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a transformative force, offering innovative solutions to enhance cervical cancer screening, improve patient outcomes, and streamline healthcare processes.
Understanding Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer primarily arises from persistent infection with high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV), a common sexually transmitted infection. While HPV infection is widespread, not all infections lead to cancer. Risk factors for developing cervical cancer include smoking, a weakened immune system, long-term use of oral contraceptives, and having multiple childbirths.
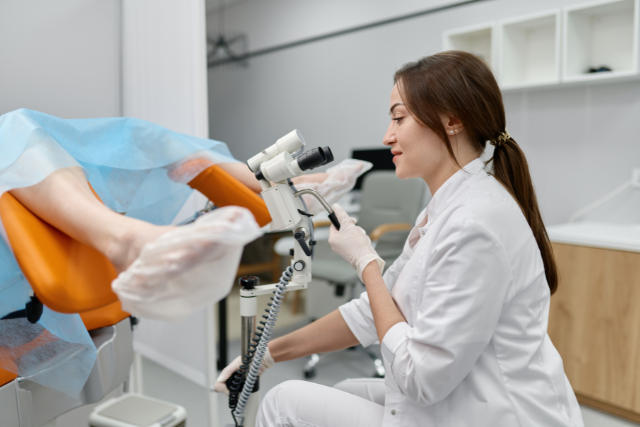
Cervical cancer progresses slowly, often beginning with pre-cancerous changes detectable through regular screening. There are two main methods for cervical cancer screening: Pap smear tests (cervical cytology) and HPV testing. The introduction of HPV vaccines has also shown promise in reducing the incidence of cervical cancer by preventing the most common high-risk HPV infections.
Challenges in Cervical Cancer Screening
Despite the availability of effective screening methods, numerous challenges persist in cervical cancer detection:
- Backlogs and Resource Limitations: Many healthcare systems face backlogs in screening due to insufficient resources, including a shortage of trained personnel and screening facilities. This is particularly pronounced in low- and middle-income countries, where access to healthcare services can be limited.
- False Negatives: The traditional Pap smear test, while effective, is not infallible. Studies suggest that Pap smears can yield false-negative results, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: Many women, particularly in underserved communities, may lack awareness of the importance of regular cervical cancer screenings or may face barriers to accessing care, including cultural stigmas or logistical challenges.
- Inequities in Healthcare Access: Disparities in healthcare access often lead to inequitable outcomes in cervical cancer detection and treatment, disproportionately affecting marginalized populations.
The Promise of AI in Cervical Cancer Screening
AI has the potential to address these challenges and revolutionize cervical cancer screening and treatment. Here are several ways in which AI can contribute to improved cervical cancer outcomes:
1. Enhanced Screening Accuracy
AI algorithms can analyze cervical cytology samples more accurately than traditional methods. Machine learning techniques can be trained on large datasets of labeled cytology images, allowing AI systems to recognize patterns associated with pre-cancerous and cancerous cells.
- Case Study: A study published in JAMA Oncology demonstrated that an AI model developed by researchers could correctly identify high-grade cervical lesions in Pap smear samples with an accuracy comparable to expert pathologists. This capability can significantly reduce the rate of false negatives and improve the overall effectiveness of screening programs .
2. Automation of Screening Processes
AI can automate the screening process, helping to alleviate the workload on healthcare professionals. By integrating AI systems into screening laboratories, clinicians can focus their efforts on cases that require human intervention while allowing AI to handle routine evaluations.
- Efficiency Gains: Automation of routine tasks, such as analyzing Pap smear samples, can expedite the screening process, allowing healthcare facilities to manage backlogs more effectively and serve more patients.
3. Risk Stratification and Personalized Treatment
AI can analyze patient data, including screening results, medical history, and demographic information, to identify individuals at higher risk for cervical cancer. This information can guide healthcare providers in developing personalized treatment plans and monitoring strategies.
- Predictive Analytics: By combining data from multiple sources, AI systems can predict the likelihood of developing cervical cancer, enabling proactive intervention for high-risk patients. This personalized approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that patients receive the appropriate level of care based on their risk profile.
4. Improving Access to Care
AI-powered telemedicine solutions can enhance access to cervical cancer screening and education, particularly in underserved communities. Through virtual consultations, healthcare providers can reach patients who may face barriers to in-person care.
- Telehealth Solutions: AI chatbots and virtual health assistants can educate women about the importance of cervical cancer screening, help them schedule appointments, and provide reminders for follow-up care. This approach can increase awareness and encourage more women to participate in screening programs.
5. Data Integration and Population Health Management
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data can support population health initiatives aimed at reducing cervical cancer disparities. By identifying trends and patterns in screening rates and outcomes, healthcare systems can implement targeted interventions to improve access and quality of care.
- Health Equity: AI can help identify populations with low screening rates and high incidence of cervical cancer, allowing public health officials to design tailored outreach programs and allocate resources where they are most needed.
Addressing Potential Concerns with AI in Cervical Cancer Screening
While AI offers significant advantages in cervical cancer screening, there are important considerations to address:
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI in healthcare raises concerns about the privacy and security of patient data. Ensuring compliance with regulations, such as HIPAA, is essential to protect sensitive information.
- Bias in AI Algorithms: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases if they are trained on non-representative datasets. Ensuring diversity in training data is crucial to developing equitable solutions that serve all populations effectively.
- Integration into Clinical Workflows: Successfully implementing AI into existing clinical workflows requires careful planning and training for healthcare providers. Ongoing education and support are essential for maximizing the benefits of AI technologies.
AI has the potential to revolutionize cervical cancer screening and treatment, addressing longstanding challenges and disparities in women’s health. By enhancing screening accuracy, automating processes, and improving access to care, AI can help ensure that cervical cancer is detected early and managed effectively.
As the healthcare industry continues to embrace AI, it is crucial to prioritize inclusivity and ethical considerations. By addressing data privacy, algorithmic bias, and integration challenges, we can harness the power of AI to improve outcomes for all women and make significant strides in the fight against cervical cancer.
The path forward involves collaboration among healthcare providers, technology developers, and policymakers to create a future where cervical cancer screening is efficient, accessible, and effective for everyone.